Sales to customers is conducted in many ways depending on the product or service. Many pricing models exist. What I would like to say is that there are four variables of conductance in every transaction. They are:
- Potential: Sales Price per Unit φ
- Number of Units N
- Time frame of delivery τ
- Conductance (Offer): Volume per Price σ
The Conductance Equation describes the specific terms of agreement for the exchange of energy with the customer or supplier. When each variable is agreed then business is conducted like so:
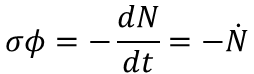
The time of delivery tau can be today, now, in 1 week. With inventory available, the time can be now.
There is an extraordinary relationship between N and φ. Many times products are sold at lower price when N is large (blue). In auctions (orange) the highest bidder gets allocated the most N and these conductance rules exhibit entirely different Price Volume elasticity.
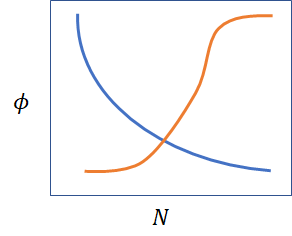
The rules of conductance drive the Elasticity of prices. Yet in every case the businesses want to produce maximum sales φ N. Both types of business must look for a better measure of of performance that will maintain sales volume. It is best for businesses to consider all energies when they make goals.
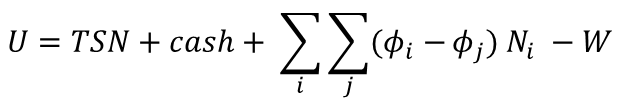
Businesses with small number of customers must build the potential energy TSN that will stabilizes prices during disruptions. It seems reasonable that the time period τ calculating TSN should be the recent period (perhaps trailing twelve months) which will best represent current customer goodwill.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.